Definition:
Equilibrium is: “1. a state of rest or balance due to the equal action of opposing forces. 2. equal balance between any powers, influences, etc.; equality of effect. 3.mental or emotional balance; equanimity: The pressures of the situation caused her to lose her equilibrium. 4.Chemistry. the condition existing when a chemical reaction and its reverse reaction proceed at equal rates.” (http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/equilibrium).
“Neutral equilibrium means that, with a small deviation, the body remains in equilibrium. An example is a wheel rolling on a horizontal surface. If you stop it at any point, the wheel will be in a state of equilibrium. A ball lying on a flat horizontal surface is in a state of neutral equilibrium.Unstable equilibrium means that, with a small deviation of the body from the equilibrium state, forces emerge which tend to increase this deviation. A ball located at the top of a spherical projection is an example of unstable equilibrium.Stable equilibrium means that, with small deviations of the body from this state, forces or moments of forces emerge which tend to return the body to the state of equilibrium. A ball located at the bottom of a spherical deepening is in a state of stable equilibrium.” (http://en.fphysics.com/states_of_equilibrium)
Equilibrium in Physics:
In physics, equilibrium is the “the condition of a system when neither its state of motion nor its internal energy state tends to change with time.” (http://www.britannica.com/science/equilibrium-physics) Basically, if the object has no angular or linear acceleration. For a single particle, the sum of the forces must be equal to 0 in order to be in equilibrium. For a rigid body, the sum of the torques and the forces acting upon the object must be equal to 0.Equilibrium in Thermodynamics:
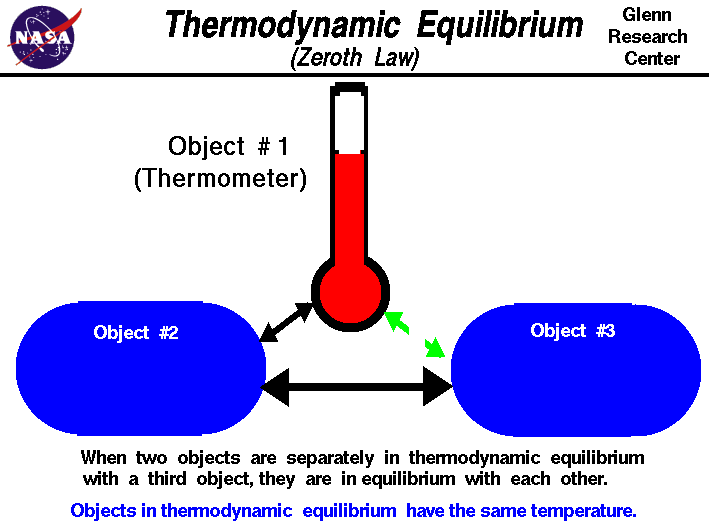 Thermodynamic equilibrium requires that objects must have the same temperature. (https://www.grc.nasa.gov/www/k-12/airplane/thermo0.html).
Thermodynamic equilibrium requires that objects must have the same temperature. (https://www.grc.nasa.gov/www/k-12/airplane/thermo0.html).Equilibrium in Chemistry:
Chemical equilibrium is “a state of balance between a pair of forward and reverse chemical reactions. A double arrow in a chemical equation… indicates equilibrium. In equilibrium, “the rate of the forward reaction (left to right in the equation) is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction (right to left).” (http://www.worldbookonline.com/student/article?id=ar183500&st=equilibrium#tab=homepage).In chemistry, there is a forward reaction and a reverse reaction. “Equilibrium refers to equality of forward and reverse reaction rates, not of quantities of reactants and products…Some reactions establish equilibrium after the formation of only minute amounts of products. In others, only minute amounts of reactants remain at equilibrium. The composition of the equilibrium mixture is sometimes referred to in terms of equilibrium position.” (http://www.avogadro.co.uk/chemeqm/chemeqm.htm).
The Equilibrium Constant:
“A reaction's equilibrium constant, Keq, measures the extent to which reactants are converted to products by the reaction. Equilibrium constants are found by multiplying the concentrations of the reaction’s products raised to the power of their stoichiometric [describes quantitative relationship between two or more chemical substances undergoing physical or chemical change] coefficients divided by the multiplication product of the concentrations of its reactants raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients.”
(http://www.chemicool.com/definition/equilibrium_constant.html).
Equilibrium in Economics:
Economic Equilibrium is “a condition or state in which economic forces are balanced. These economic variables will be unchanged from their equilibrium values in the absence of external influences. Economic Equilibrium may also be defined as the point where supply equals demand for a product- the equilibrium price is where the hypothetical supply and demand curves intersect.” (http://www.investopedia.com/terms/e/economic-equilibrium.asp). In more simplistic terms, “equilibrium = equality of the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded; a state in which neither prices or quantities show any tendency to change.” (http://www.pitt.edu/~mgahagan/Definitions/LawofMarkets.pdf).
Other Types of Equilibriums:
Equilibrioception, “or sense of balance is one of the physiological senses…broadly defined, a sense is a mechanism or faculty by which a living organism receives information about its external or internal environment…the sense of balance reflects an awareness of equilibrium involving the perception of gravity. It helps prevent humans and animals from falling over when walking or standing still.” (http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Equilibrioception).
Genetic Equilibrium is “the condition of a dynamic genetic system in which the several rates of change between all possible pairs of parts are such that the composition is invariant.” (http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/genetic+equilibrium).
Homeostasis is “the tendency of a system…to maintain internal stability, owing too the coordinated response of its parts to any situation or stimulus that would tend to disturb its normal condition or function.” (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_types_of_equilibrium).
Punctuated Equilibrium is a theory in evolutionary biology. It was first proposed by Steven Jay Gould and Niles Eldridge. It is a useful model for a kind of evolutionary change.Sedimentation Equilibrium is an “analytical ultracentrifugation method for measuring protein molecular masses in solution and for studying protein-protein interactions.” (http://www.ap-lab.com/sedimentation_equilibrium.htm).
Equilibrium Theory is the “theoretical relationship between immigration and extinction of species to islands, depending on their size and distance from the mainland or other species source.” (http://www.snre.umich.edu/~dallan/nre220/outline15.htm).
Equilibrant Force “is a vector that is the exact same size as the resultant would be, but the equilibrant points in exactly the opposite direction.” (http://www.studyphysics.ca/newnotes/20/unit01_kinematicsdynamics/chp06_vectors/lesson24.htm).
Equilibrium Mode Distribution is the “condition in a multimode fiber wherein after propagation has taken place for a certain distance.” (https://www.atis.org/glossary/definition.aspx?id=7757).
Hydrostatic Equilibrium is the “the principle…that the pressure of any point in a fluid at rest…is due to the weight of the overflying fluid.” (http://www-rohan.sdsu.edu/~aty/explain/thermal/hydrostatic.html).
Mechanical Equilibrium is “the state of a mechanical system in which the sum of the forces on each particle of the system is zero.” (http://encyclopedia.kids.net.au/page/me/Mechanical_equilibrium).
“Radiative equilibrium assumes that incoming radiative energy from the Sun is equal to the outgoing radiation emitted by the planet: incoming energy=outgoing energy.” (https://www.google.com/webhphl=en#hl=en&q=radiative+equilibrium).
Diffusion equilibrium is “the state in which the concentrations of the diffusing substance in two compartments are the same or become equal.” (http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Diffusion_equilibrium).
Thermal Equilibrium is when “objects are at the same temperature and there is no heat transfer.” (http://www.physics.louisville.edu/cldavis/phys298/notes/heat_thermeq.html).
Dynamic Equilibrium is “the reaction rate of the forward reaction is equal to the reaction rate of the backward reaction.” (http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/Core/Physical_Chemistry/Equilibria/Chemical_Equilibria/Principles_of_Chemical_Equilibria/Dynamic_equilibrium).
Equilibrium constant “K, expresses the relationship between products and reactants of a reaction at equilibrium with respect to a unit.” (http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/Core/Physical_Chemistry/Equilibria/Chemical_Equilibria/The_Equilibrium_Constant).
Equilibrium price is “the price at which the quantity of a product offered is equal to the quantity of the product in demand.” (http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/equilibrium-price).
Intertemporal equilibrium is “the economic theory that believes it is not possible to correctly analyze the equilibrium of the economy from a single fixed point in time.” (http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/intertemporal-equilibrium.html).
Sources:http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/equilibriumhttp://www.britannica.com/science/equilibrium-physicshttp://www.brighthubengineering.com/thermodynamics/4720-what-is-thermodynamic-equilibrium-part-one/http://www.worldbookonline.com/student/article?id=ar183500&st=equilibrium#tab=homepagehttps://www.grc.nasa.gov/www/k-12/airplane/thermo0.htmlhttp://en.fphysics.com/states_of_equilibriumhttp://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Equilibrioceptionhttp://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/genetic+equilibriumhttp://dictionary.reference.com/browse/homeostasishttp://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/03/5/l_035_01.htmlhttp://www.studyphysics.ca/newnotes/20/unit01_kinematicsdynamics/chp06_vectors/lesson24.htmhttp://www.ap-lab.com/sedimentation_equilibrium.htmhttp://www.snre.umich.edu/~dallan/nre220/outline15.htmhttps://www.atis.org/glossary/definition.aspx?id=7757http://www-rohan.sdsu.edu/~aty/explain/thermal/hydrostatic.htmlhttp://encyclopedia.kids.net.au/page/me/Mechanical_equilibriumhttp://dictionary.reference.com/browse/thermodynamic-equilibriumhttp://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Diffusion_equilibriumhttp://www.physics.louisville.edu/cldavis/phys298/notes/heat_thermeq.htmlhttp://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/Core/Physical_Chemistry/Equilibria/Chemical_Equilibria/Principles_of_Chemical_Equilibria/Dynamic_equilibriumhttp://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/Core/Physical_Chemistry/Equilibria/Chemical_Equilibria/The_Equilibrium_Constanthttp://www.investopedia.com/terms/e/economic-equilibrium.asphttp://dictionary.reference.com/browse/equilibrium-pricehttp://www.investopedia.com/terms/g/general-equilibrium-theory.asphttp://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/intertemporal-equilibrium.htmlhttp://www.chemicool.com/definition/equilibrium_constant.htmlhttp://www.pitt.edu/~mgahagan/Definitions/LawofMarkets.pdf

No comments:
Post a Comment